Can you have pneumonia and bronchitis at the same time?

Yes, it is. Bronchitis and pneumonia at the same time can happen if the infection spreads from the bronchial tubes to the lungs or a secondary infection occurs. If you have symptoms of bronchitis, and it stays for more than 3 weeks it is better to see a doctor.
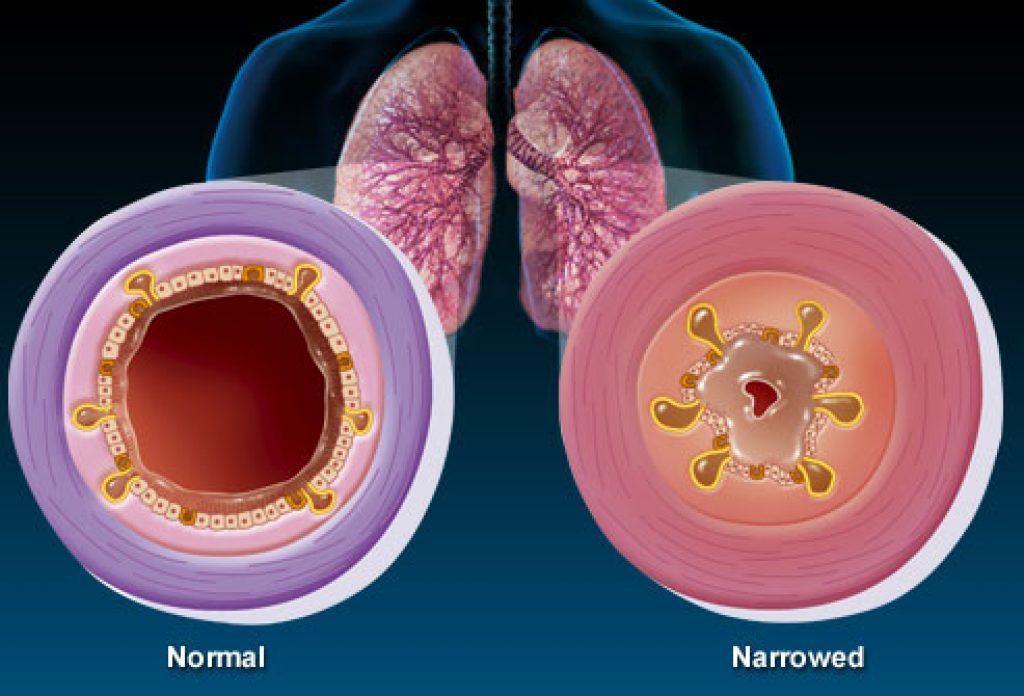
Bronchitis is basically an inflammation of the airway passage in our lungs and it can be due to several factors but most commonly like a cold or even flu viruses.
Acute bronchitis generally lasts about one to three weeks whereas chronic bronchitis you would find more where the patients would have some symptoms more of as of coughing and shortness of breath more than three months at a time.
Also, they can persist to have these symptoms for several years as far as a contagious you would find that the reasons for acute bronchitis to be more contagious.
If you are affected by acute bronchitis then your recovery time is within 10-14 days depending on your immune system and proper nursing. Some may have to endure this condition until three weeks also.
It will take longer for those who are affected by chronic bronchitis as a result of COPD. This may register in the body and last for about three months.
The commonest sign of bronchitis is the sound you make during coughing. The coughing sounds wheezing in most cases due to congestion in the chest by mucus.
It appears that the blocked lung and air passage causes the rattling and whistling noise when you try to breathe in or out.
The answer to the question above depends simply on the type of bronchitis condition one has developed.
In acute bronchitis, the symptoms may wane on its own within 10-14 days or three weeks at best upon proper rest, diet, and lifestyle.
Things may get complicated if you develop chronic bronchitis which requires administering antibiotics and a health-expert guideline.
Read More: Can you die from bronchitis if not treated?
Usually, patients who present with shortness of breath coughing are very common low-grade temperatures.
And sometimes you will have some chills associated with it and sputum production,
Sometimes, bronchitis often occurs after a cold or the flu.
Why is that?
Because, when you’re having flu-like symptoms you’re finding yourself caught them quite a bit and a lot of
times that irritations to our lungs particularly the air passageway you’ll have some inflammation that would give rise to bronchitis.
Below are some of the symptoms you may encounter when exposed to bronchial condition:
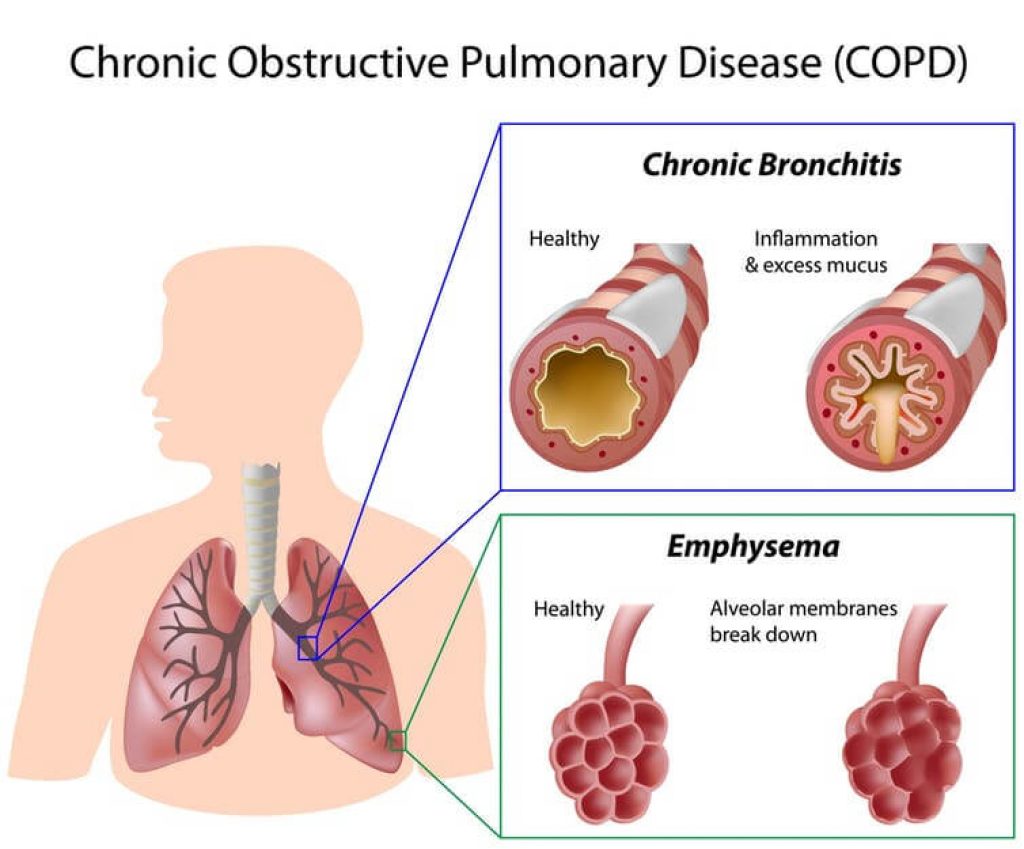
This one is COPD “chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.” It’s a common preventable and treatable lung disease and the typical symptoms that you’ll see in patients with emphysema C.O.P.D. is shortness of breath, and you’ll also see cough, and if it’s wet you’ll have sputum as well.
These are very nonspecific symptoms, but they’re very typical of what you see in C.O.P.D.
1. heart disease and
2. cancer
3. COPD
COPD actually went up from about 2007 to 2010 all the others(Heart disease and cancer) have gone down in frequency
A couple of statistics that you should know is it’s the third most common cause of death.
In the US; pretty significant. C.O.P.D or emphysema is a disease that affects the lungs.
In addition to all of this, it’s also the second leading cause of disability.
In case of course, you’re wondering how much of this costs the US healthcare system in the United States every year?
The answer is about 50 B!
Specifically, if you were to take a look your lungs, you, of course, know that your lungs have 2 sides and that there’s a major airway call the trachea and it branches off into the right and left main-stem bronchus.
From there it just goes down to smaller and smaller branches, without getting into too much anatomy.
If we were to take these very small bronchioles or respiratory bronchioles they would eventually end in a grape-like cluster called an alveolus.
This essentially increases the surface area.
This is what normal respiratory bronchioles would look like.
If you were to take all these alveoli in the entire lung and spread it out it would be about the size of a tennis court.
It’s pretty big.
Now C.O.P.D. affects 2 main areas.
It affects this bronchus, the small bronchial and it also affects the alveolus in a bad way.
The surface area becomes much smaller and all these changes happen throughout the lung,
but mostly in the upper regions of the lung.
As a result of that it’s hard to get the air out.
There’s an obstruction, that’s the key point here is that air cannot get out of the lungs.
That’s why it’s called chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
In addition to that, because these alveoli are all destroyed and become areas of large balloons. The length actually increases in size and as a result of that you get these patients with large lungs but they’re full of air and they can’t get the air out and that’s basically C.O.P.D.
The way that we diagnose C.O.P.D. is based on this obstruction.
Let’s review.
C.O.P.D. is
1) common, it costs a lot;
2) it’s the third leading cause of death and is the only 1 of the 5 that are actually increasing in frequency;
3) causes difficulty with breathing out, that’s obstruction;
4) reduces the cross-sectional surface area, causes drops in oxygen;
5) you diagnose it by spirometry.
Source: by Dr. Roger Seheult of http://www.medcram.com.
Pneumonia is the condition when the alveoli or the air sacks in your lungs are congested with fluid caused by infection. Either one or both lungs may get affected by pneumonia.
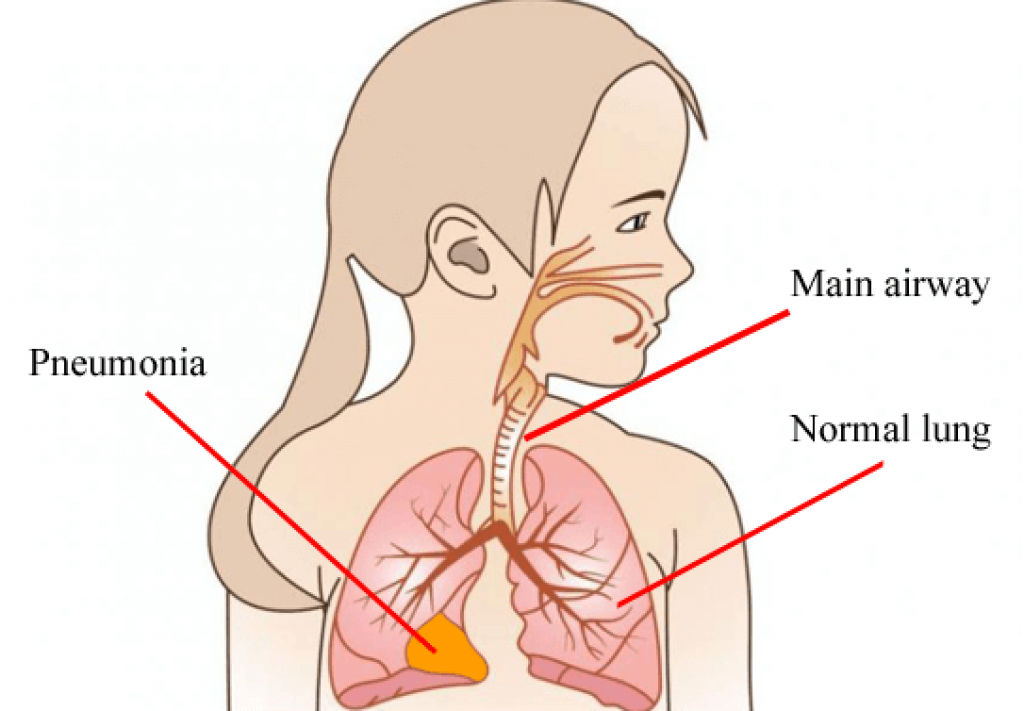
Pneumonia is a result of your lungs affected by fungi, virus, or bacteria. Your air sacs may get flamed due to these affects. Older people are more vulnerable than younger and healthy people to pneumonia complications.
Pneumonia can be life-threatening. It is no surprise that in the United States alone, about 1 million people per year pay visit to clinics for medical attention to their pneumonia condition. Sadly enough, about fifty thousand of the affected people die from pneumonia each year.
The early signs of pneumonia are as follows-
Symptoms of pneumonia start with the breathing difficulty and coughing. There are other signs that follow the initial symptoms. Find them below:
Pneumonia has four stages–
Ist stage-consolidation,
2nd Stage red hepatization,
3rd stage grey hepatization and
4th stage resolution.
Every year, it kills an estimated 1.4 million children under the age of five years.
Children can be the victim of pneumonia due to other lung infections. Viral or bacterial infections can also cause the pneumonia symptoms in babies.
The small air sac in the lung gets swollen due to mucus or sticky fluid and obstructs air passing through the line. The babies find it hard to breathe.
Proper medical attention may help babies recover from the condition.
You should be careful from the moment you realize your child has caught cold.
Pneumonia often comes after cold. You might mistake the pneumonia signs as normal cold condition but they may not.
Remember, pneumonia symptoms may start within 2-3 days from the first cold attack.
Signs of pneumonia may show up depending on the type of virus or bacteria causing the infection.
Below are some common signs and symptoms of pneumonia in babies:
Pneumonia is the worsened condition of cold that gives your baby a hard time.
Medically known respiratory viruses such as Influenza A (Flu A), respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), adenovirus (ADV) and human metapneumovirus (HMPV), and bacteria such as Streptococcus pneumoniae, Hemophilus influenza, Staphylococcus aureus, and Mycoplasma pneumoniae (Mp) can cause pneumonia in childhood [Source: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6788033/].
If your child’s lungs were already infected previously by cold and left untreated, chances are it may catch pneumonia quickly on the various pollutant exposures.
Often parents overlook the hygienic matters for which children catch various germs from the floor, toys, foods, and on whatever places they toddle or crawl.
Germs like virus, bacteria, parasites, or fungi may creep into their delicate nasal line during breathing. Your babies can possibly swallow stuffs without your notice that may carry bacteria. Such residues may enter the lungs from the stomach and affect the air sacks eventually.
Older kids and teenagers are prone to Mycoplasma which makes them suffer with rash, sore throat, or headache in addition to pneumonia condition.
Kids may develop pneumonia symptoms from whooping cough. Having affected by so, they experience long coughing duration, their face going blue for the lack of oxygen, and sound “whoop” while breathing.
Pregnant women are among the higher risk-borne group caused by pneumonia.
Expecting mothers should not neglect the tiniest signs of pneumonia and see the doctor immediately.
Pregnant women may catch pneumonia due to weak immune system. Besides their lung capacity may reduce because of the expansion of their uterus.
Following are some common causes of pneumonia during pregnancy:
Pregnant women may develop bacterial pneumonia in one of their lungs or a part of their lung. Common bacteria that cause the pregnant woman’s lung having pneumonia are haemophilus influenza, streptococcus pneumonia, and mycoplasma pneumonia.
It is common to get your lung infected by viral pneumonia during pregnancy. Viruses that cause pneumonia are Influenza virus, acute respiratory syndrome, and varicella.
Most rarely, in the third trimester, women may catch fungal pneumonia caused by fungus Coccidioidomycosis.
Common symptoms of pneumonia that may occur in pregnant women are:
The risk of pneumonia during pregnancy seems lowest in the first trimester with only 0–16% of cases occurring during this period.
Following are risks factors that may lead to pneumonia:
[Source: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1746055/pdf/v056p00398.pdf].
If the mother has pneumonia, she and the expected, the coming child, both will have complications.
Below are few of the complications they can encounter:
Baby’s Complication:
As we know, bronchitis can invade your lungs because of virus, fungi and bacterial exposure. So your primary preventive measure must be avoiding the source of these malice.
A healthy and hygienic lifestyle may save you significantly from bronchial complications.
You may follow the guidelines below for preventing bronchitis condition:
[Source: https://www.cdc.gov/antibiotic-use/community/downloads/Flyer-Bronchitis.pdf]
Because of the rush of modern lifestyle, you may not be able to keep up with everything stated above. Still, consulting your doctors about your and your child’s lungs at least bi-monthly or monthly should not be a hard task.
Among many types, bacterial pneumonia is the most dominating and on many occasions, fatal.
Babies below 2 and adults over 60’s are at more risk of pneumonia infection and its fatality.
The United States file about one million pneumonia cases each year out of which 50,000 (approx.) end up to death [Source]
Preventive guideline and actions are similar to prevention of bronchitis since both originate from cold and both affect lungs.
Concomitant risk factors should be avoided in order to keep pneumonia at bay.
One cannot be too hopeful to recover fully by vaccines. But the shots will reduce the intensity of the pneumonia and help you fight through the complications.
Vaccines are mainly applicable for those who have weakened immune system due to previous infections or bad lifestyle such as chain-smokers or heavy drinkers. The other group who may need vaccines is those with less capability to fight on like older people over 65 or children below 2.
Clinics and hospitals may give you two types of shots for preventing bacterial pneumonia. Those are:
Both the above vaccinations are recommended for those who had never taken any of them before. There should be at least an 8 week gap between the two vaccines starting with the PCV13 followed by the PPSV23.
One should have a thorough check-up and discussion with the doctor before administering these shots.
[Source: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6385209/, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK507794/]
It’s wise to have a clear idea on the signs, symptoms, and differences among the flu, bronchitis, and pneumonia so the victims or their observers don’t mix up these three different conditions.
These three predicaments might appear similar initially but one has to look carefully into their progressive conditions.
Below, we shall try to make a comparative table of these three diseases:
| Flu/ Influenza | Bronchitis | Pneumonia | |
| Cause | Caused by Influenza A or B virus. | Caused by virus from the developed stage of common cold. | Caused by both virus and later by bacteria. |
| Affects | Affects respiratory system. | Inflames air sacs of lungs. | Infects air sacs of lungs. |
| Symptoms | Symptoms are high fever, muscle ache, persistent cough, nasal congestion, sore throat, etc. | Hard time breathing, coughing with wheezing sound, muscle ache, etc. | Chest pain, confused mental awareness, cough with phlegm, fatigue, chills, etc. |
| Duration | May last from 1 to 3 weeks. | May last for 10-14 days or more than 3 weeks. | May last for 3 weeks or carry on for a lifetime. |
| Treatment | Enough bed rest and fluid in normal cases but prescribed antiviral medicines in complicated conditions. | Enough rest and fluid, cough suppressant medicines, pain reliever medicines, etc. Antibiotics for bacterial bronchitis. | Enough bed rest, healthy lifestyle, nutritious diet, vaccinations, prescribed medicines, etc. |
| Severity | It may go away on its own but can be life-threatening for victims with weak immune system. | Acute bronchitis is curable within 3 weeks at best but chronic bronchitis may last for a lifetime. | A worldwide phenomenon disease that affect about a million people in the US only. |
Following comparative information about bronchitis and cold may come handy in treating them wisely:
| Bronchitis | Cold | |
| Cause | Caused by viral or bacterial infection in the lungs. | Caused by viral attack in the respiratory system. |
| Affect | Inflames air sacs of lungs. | Affects nasal line, throat, and chest. |
| Treatment | May go away on its own if it’s viral but may need antibiotics if it’s a bacterial bronchitis. | Since, caused by virus, antibiotics are not applicable. OTC medicines may be helpful in comforting irritations and achiness. |
| Duration | Not life compromising but may be lifelong suffering. | Infectious from one to another and go away on its own within one week or two. |
As I mentioned earlier bronchitis is more with the inflammation of the air passageway whereas pneumonia you will find that there the air sacs itself could be filled with fluids. Coughing wheezing and fatigue they’re all common symptoms of bronchitis.
Bronchitis and pneumonia can very often be confused and not just what it is but kind of the symptoms and treatment plan also. Both can cause fever chills coughing and shortness of breath they can present a
little similar.
And be hard to delineate pneumonia will usually be more severe now a lot of times both can be treated as an outpatient if you have healthy lungs.
| SL No | Bronchitis | Pneumonia |
| 1 | Bronchitis is a viral infection that often accompanies the common cold. | Pneumonia is a bacterial infection that causes fluid to escape into the lungs. |
| 2 | Typically bronchitis can resolve on its own within a week or two. | Patients with pneumonia will likely need an antibiotic. |
| 3 | Usually with bronchitis you do not need antibiotics as it’s a viral illness and it will resolve on its own and actually giving antibiotics can be a bad thing you’re exposing different bugs to the antibiotics and that’s how you get resistances. | If pneumonia is left untreated it can become very severe even life-threatening for children and the elderly. |
| 4 | A lot of people will get pneumonia with bronchitis especially if their immune system for whatever reason is already kind of compromised. | If a patient has pneumonia symptoms it’s important they visit their doctor to be diagnosed patients with asthma or COPD may need more aggressive treatment to prevent the diagnosis from getting worse. |
Watch the video: https://www.health.com/cold-flu-sinus/bronchitis-vs-pneumonia
For a contagiousness it’s hard to say because what’s actually contributing to the problem could be the viruses, a simple cold versus the flu itself so it could be from one week to even three weeks at a time.
Our smokers are those with other longer pulmonary issues more susceptible to bronchitis most.
Definitely the reason for that is because smokers with the inhalations of the irritants from the cigarettes that is a persistent exposure of irritants to the bronchioles which is the air passageway so that would definitely give rise to increased likelihood of developing bronchitis.
The rock singer Tom Petty famous was suffering from bronchitis when he died of a heart attack.
Bronchitis can definitely be like life-threatening particularly and individuals who have increased risk factors as for example Tom Petty with heart disease someone who has lung disease and as well as diabetes are immune suppression.
80 to 90 percent of the time bronchitis is due to a virus and in these settings antibiotics are not helpful to treat the total treatment.
There are some over-the-counter cough medications that can help with suppressing the cough and that is also sedating but have to be very careful with those type of medications particularly in the very young and the very old.
Who suffer from chronic bronchitis the most important thing is to be able to avoid the irritants that the individual is exposed to particularly smoking. So, the tobacco exposure is one of the main reasons for exacerbation of those chronic bronchitis. So, avoiding smoking avoiding the areas that might contribute
to irritating the lungs particularly dust. Proper treatment can exposures those type of things to help decrease those inflammations.
How does bronchitis turn into pneumonia? Or
Is pneumonia worse than bronchitis?
Bronchitis and pneumonia are 2 common conditions in the cold weather. Sometimes, symptoms can be very similar, and the 2 can overlap as well-
A lot of times when there are increase in coughing shortness of breath are even sputum productions the diagnosis of bronchitis is made clinically and for if the symptoms actually continues to persist particularly greater and several days at a time.
Acute bronchitis. About 5% of adults self-report an episode of acute bronchitis each year, and up to 90% of them seek medical advice. Viruses appear to be mainly responsible, causing up to 95% of cases of acute bronchitis in otherwise healthy adults. The viruses are the same as those that cause the common cold.
Source: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov › pmc › articles › PMC2278319
If your symptoms and sufferings wane within 2-3 weeks then you can safely identify it as a vital bronchitis. You may not need any medications since no antibiotic would apply to this.
When your bronchial condition last for more than 3 months and your doctor prescribes you the antibiotics, you are inflicted with bacterial bronchitis.
Some home remedies are applicable for bronchitis as below:
Drinking at least 8-12 glasses of water can keep up the fluidity and ease your breathing.
Remember, while mineral water enables you to cough up easily and clear your air tubes, caffeinated beverages may cause muscle fatigue and restlessness.
Drinking coffee may comfort you temporarily but drink it less.
Simmer water with camphor, eucalyptus, or pine oil. Inhale that spiced vapor for loosening the mucus and clearing your air passages of your lungs.
A humidifier is a good option for breathing in moist air during sleep. This can ease your respiratory function and comfort your nasal congestion.
One of the popular folk remedial teas is Mullen tea that clears off mucus from lungs. Try drinking it daily to ease chest congestion and breathing difficulty.
If you want your nasal congestion melt and help air inhalation, add some aesthetic spices in your foods. Adding ginger, garlic, black-pepper, cumin, cinnamon, etc. would give you a warm taste and bring your lost appetite.
Fiery dishes with pepper and other spicy ingredients would make your nose run and clear mucus in your lungs.
Typically, acute bronchitis may last for 10-14 days or up to 3 weeks depending on individual care and treatment. Chronic bronchitis may last for up to 3 months with proper antibiotic administration and healthy lifestyle. But people with weak immune system may carry the chronic bronchitis condition throughout their lives.
Usually your doctor will diagnose your bronchitis symptoms as well as listen to your chest sound with stethoscope.
The term asthmatic bronchitis is not recognized in medical diagnosis. It’s a scant colloquial phrase that is used in denoting overlap symptoms of both asthma and bronchitis.
According to Len Horovitz, MD, a pulmonologist with Lenox Hill Hospital in New York City, in one of his discussion with Health, said, “It’s really not a clear entity as a diagnosis,” “The term may have originated decades ago when medical knowledge was less advanced and diagnoses less specific.” [Source: https://www.health.com/asthma/asthmatic-bronchitis]
Occurring both asthma and bronchitis symptoms concurrently is called asthmatic bronchitis. In such case, both inflammation and narrowing of the air passages may take place which make breathing quite difficult.
It’s hard to determine how long the asthmatic bronchitis would last- it may be about 10-15 days, or 3 weeks, or a couple of months.
Since asthmatic bronchitis is a combination of two different conditions, it simply depends on the number of symptoms one has developed, the strength of immune system one possesses, and the kind of treatment he or she is taking, for determining the longevity of it.
Asthmatic bronchitis or bronchial asthma may be treated in two ways:
[Source: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2696883/]
The basic difference between these two conditions is that-
The bronchitis solely will inflame your air passages of lungs with fluid and make it harder every day for you to breathe.
The asthmatic bronchitis may have variable symptoms due to the overlap effects of asthma and bronchitis including inflammation, infection, or narrowing of your air lines of the lungs.
There are 6 types of asthma based on various triggers:
Asthma and bronchitis have their remarkable individual effects on people. When both these overlap and act in combination, things may be more sensitive and sometimes severe for those who suffer from it.
The delicate victims should maintain suitable physical exercise, diet, residential environment, and workplace in order to keep the asthmatic bronchitis attack in control.
Things may get serious if the proper lifestyle and medicine are not followed. Kids under 2 and older people after 60’s are more prone to severe asthmatic bronchitis symptoms.
Answer: Acute Bronchitis that last for 10-15 days or sometimes for 3 weeks and Chronic Bronchitis that may effect and last for about 3-4 months.
Answer: Bacterial attack in the airways of lungs is the primary cause of chronic bronchitis.
Answer: Acute bronchitis is contagious as it originates from virus. It’s transferrable through handshakes, sneezing, talking, coughing, and exhaling.
Answer: False; airways are mostly affected by bronchial complications, so it is necessary to clear the airways and suppress constant coughing.
Answer: True.
Take the Bronchitis Quiz First In here- BRONCHITIS QUIZ
Another Part of Bronchitis Quiz
4 Questions to Determine If You Have Bronchitis
Research taken from Dr. Mehmet Kesimer and co-author Richard Boucher, MD.
How to Tell If Bronchitis Is Turning Into Pneumonia and Tips
Bronchitis vs. Pneumonia: Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis
Bronchitis vs. Pneumonia: The Difference Between Them
How to Tell If It’s Bronchitis Or Pneumonia – Symptoms
When does a cough turn into pneumonia
Bronchitis vs. Pneumonia: Here’s How to Tell the Difference
Can You “Catch” Bronchitis or Pneumonia from Someone Else
Walking Pneumonia Versus Bronchitis – News-Medical.Net
 |
 |
 |
 |
Great Ones for You