Arthritis is a prevalent condition that is frequently overlooked. Essentially, the term "arthritis" does not refer to a particular diagnosis; rather, it is a colloquial term for joint soreness or sickness. There are over a hundred different kinds of arthritis and diseases that are associated with it. Arthritis occurs throughout the world, genders, and ethnicities, and it is the biggest source of disability in the United States. Inflammation, discomfort, rigidity, and reduced flexion are all significant arthritic joint sensations. Symptoms usually develop and just go. They are classified as mild, strong, or chronic. They may remain stagnant for decades, although they might develop and worsen with time. Persistent discomfort, incapacity to do everyday tasks, and difficulty walking or taking the stairs are all symptoms of degenerative arthritis. Arthritis can result in long-term musculoskeletal abnormalities. Although some structural alterations are apparent, such as bulbous hands and wrists, the deterioration is typically only evident on X-rays. Arthritis can affect the brain, vision, breath, kidneys, and epidermis in addition to the joints.
Contents
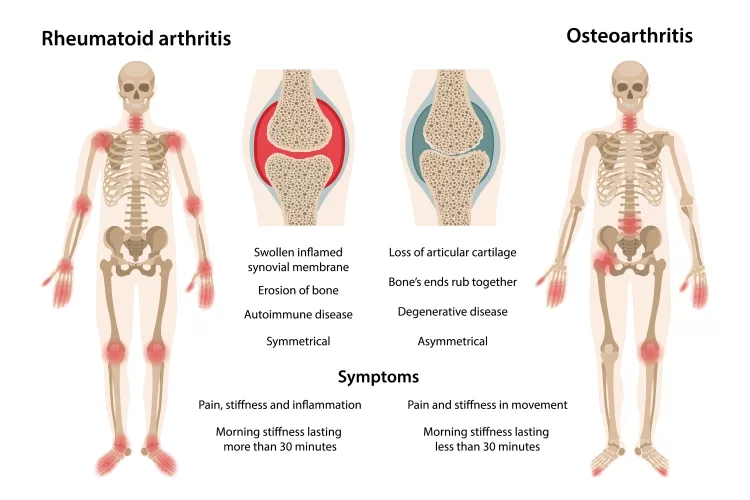
Arthritis is a widespread illness characterized by muscle spasms and discomfort that impacts more than half a million people and 3 million children in the United States. There seem to be over 100 distinct kinds of joint pain, as per the Arthritis Foundation. The following are a few of the most frequent:
The joint's protecting cushioning wears away, making the activity more complex as well as unpleasant. Whenever cartilage deteriorates, the bones of the joint may grind one against another, producing tremendous agony. Osteoarthritis is the main classification of degenerative arthritis. In osteoarthritis, pain totally depends in terms of severity in individuals and can vary from moderate to very high.
It is beneficial to have a strong immune system to get clearance of bacteria as well as other microorganisms and to prevent illness. This type causes additional aggravation. However, the immune response may go haywire and wrongly target joints with unmanaged aggravation, causing potential bone loss as well as harming inner organs, eyes, and other body components.
Some of the most common types of inflammatory arthritis are rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and lupus.

The disease can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungus entering the joint. Throughout many cases, prompt antimicrobial treatment helps cure bone inflammation, although arthritis can develop into a chronic condition. One type of infectious arthritis amongst many is called fibromyalgia. Fibromyalgia is a painful condition that affects the central nervous system. This implies that pain signals are reprocessed in the central nervous system than they are normally. A contactor action that normally causes no pain might become unpleasant; whereas, something that is already unpleasant can become considerably more painful. It is characterized by generalized pain throughout the body.
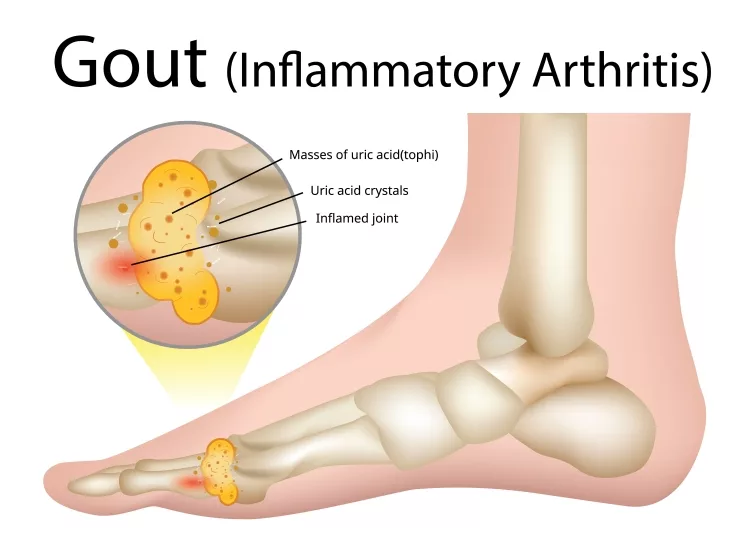
Purines, a certain type of chemical found in human bodies and also many foods, are broken down by the enzymes present in our body, resulting in uric acid formation. Some individuals have an excessive uric acid presence because their bodies create more acid than how much they need, or sometimes, they can't get rid of it rapidly either. In certain patients, uric acid accumulates in the joint and produces syringe crystals, resulting in abrupt bursts of excruciating aches and pains, often known as a type of metabolic arthritis.
One of the most common metabolic arthritis is Gout. Since gout is pretty common as well as commonly misunderstood, we are going to make it the main focus of our topic today.
Gout is a kind of inflammatory arthritis; however, unlike rheumatoid arthritis or psoriatic arthritis, it does not produce widespread inflammation. Gout generally affects the toes, but it can damage other bones as well. Gout may appear and go in phases, or it might become persistent if uric acid levels aren't lowered, experiencing discomfort and impairment.
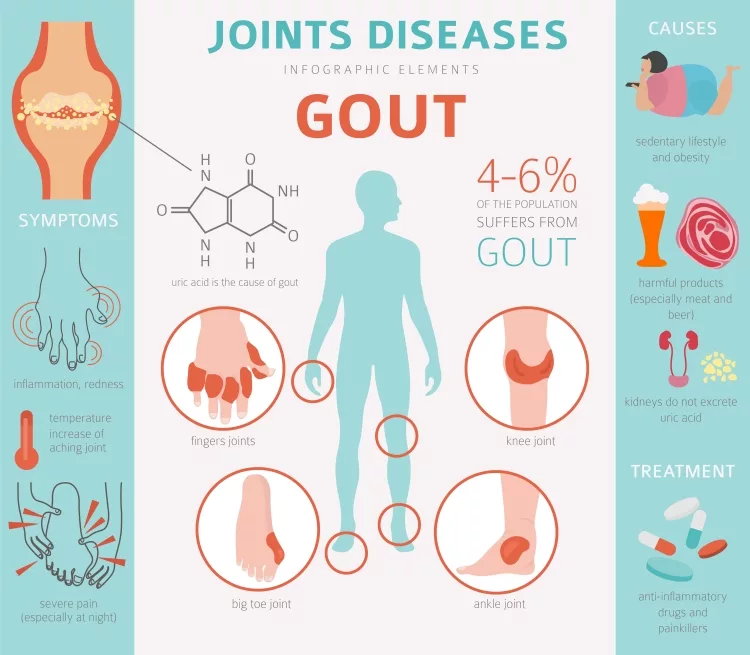
Gout is by far the most prevalent form of inflammatory arthritis in men, affecting over three million Americans. Females are, however, more prone to get gout after menopause, despite the fact that the disease affects them less in general as compared to men.
Gout episodes can strike suddenly and may reoccur over periods. This continuous reappearance can induce oxidative stress in the inflammatory region over time and can be excruciatingly agonizing. Gout is caused by hypertensive conditions, coronary artery diseases, and adiposity.
Here is a detailed video on what is gout:

Gout, being a type of arthritis itself, is further classified into various types. These types are based on how the gout attack tends to progress. They are discussed in detail below:
A person's levels of uric acid might be high without causing any indications. Although most people do not require therapy at this time, excessive uric acid concentration in the body can damage blood vessels that are not visible. As a consequence, a doctor might counsel a patient with high uric acid measures to promote the identification issues that may be contributing to the accumulation of the acid.
Whenever urate crystals in a bone produce an inflammatory response and muscle spasms, this stage develops. This abrupt assault is known as a "flare,"and it can linger anywhere from 3 days to several months. Flare-ups may be exacerbated by unpleasant life events and heavy drinking habits.
This stage begins amid acute gout episodes. These periods get narrower when an individual's gout gets worse. Urate crystals might keep growing up in mucosa between such times.
Chronic tophaceous gout is perhaps the most agonizing kind of gout, and it can cause lifelong bone and kidney damage. Patients with chronic gout and tophi in colder portions of the body, including the bones of the hands, might form tophi during this phase. After several years of acute gout episodes, chronic tophaceous gout develops. Recipients of adequate therapy, on the other hand, are unlikely to reach this level.
Calcium pyridine phosphate deposition often referred to as pseudogout, is a disease that professionals frequently misinterpret as gout. Pseudogout has indications that are extremely similar to gout, but the flare-ups are generally lower extreme. The main distinction between gout and pseudogout would be that calcium phosphatidyl crystals, not urate crystals, aggravate the joints. Pseudogout is treated differently from gout.
Gout is the most prevalent kind of arthritis. Children are seldom afflicted by elderly adults.
Males are four times more likely than females to develop gout among persons under the age of 65. In patients over the age of 65, this proportion marginally falls to four trials as probable.
A person's risk of acquiring gout is increased if they have a family history of the disease.
The elimination of uric acid from the body is hampered by alcohol intake. Consuming an elevated diet in purine presence also raises the uric acid balance in the bloodstream. Both of these things can cause gout.
Chronic lead exposure has been implicated in the development of gout in research.
Certain medicines can raise the uric acid balance in the bloodstream. Some diuretics and salicylate-containing medications fall into this category.
Gout is associated with being severely obese, as well as possessing high amounts of subcutaneous fat mass. Being overweight and obese, on the other hand, does not cause the disease directly.
Kidney impairment as well as other renal diseases can impair your body's capacity to eliminate waste, resulting in high uric acid levels. Hypertension and diabetes are two more diseases linked to gout.
Certain illnesses have no indications whatsoever. For instance, a person may even have high cholesterol for decades while realizing it, and even certain malignancies don't show signs until they're advanced. These would be referred to as asymptomatic disorders, and while symptoms are frequently associated with distress or faulty function, an illness lacking symptoms can be fatal.
Several infections go undetected for long periods of time. These would be known as preclinical infections, and they can be infectious even though the individual with the infection has no visual signs. Mostly during the initial cycle, or the time when the pathogen takes control of the person, the illness might still spread from person to person. Several infections go undetected for long periods of time. These would be known as preclinical infections, and they can be infectious despite the fact that the individual with the infection has no visual signs. Mostly during initial cycle, or the time when the pathogen takes control of the person, the illness might still spread from person to person.
This is why it is important to know the indications of the condition that you suspect going through so that you can come to the most relevant and sensible conclusion. Some of the most common signs and symptoms that indicate that you have gout are briefly discussed below:
Arthritis is among the most common complications of joint discomfort. Osteoporosis (OA) and psoriatic arthritis (RA) are really the two most common types of arthritis (RA). This becomes more frequent in individuals over the age of 40, as per the American College of Rheumatology. It causes inflammation and usually affects joints that are used often, such as the fingers, elbow, pelvis, and knee.
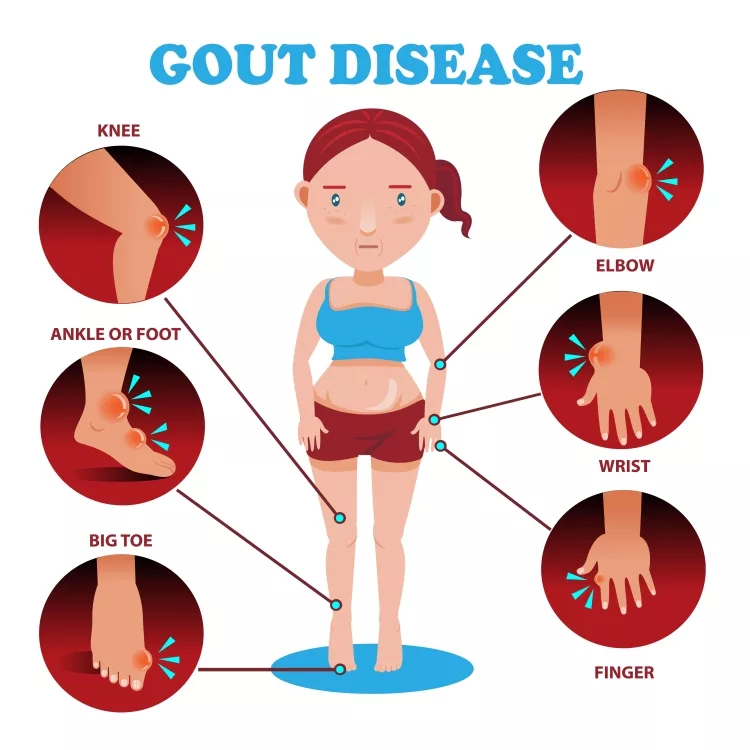
Gout is most commonly associated with the big toe, but this can damage any bone. Limbs, elbows, shoulders, wrists, and fingers are among the other joints that are often afflicted. The soreness would also most likely be the worst throughout the first four to twelve hours after it starts.
Each symptom might have another originating point, getting confused with some other disease. If you are only having joint pain, it might be due to some other reason, and not necessarily arthritis. Other conditions that cause similar joint pain include lupus, tendonitis, chondromalacia of the patella (also known as the knee-cap's cartilage breakdown), sarcoidosis, etc.
Chronic pain is discomfort that can last for more than twelve weeks. The pain might be severe or mild, and it can feel like it's blistering or hurting in the afflicted regions. It might be constant or periodic, appearing and disappearing for no obvious cause. Chronic pain may strike almost any region of the body. In the many afflicted regions, the pain might feel completely different.
In a patient suffering from gout, residual joint soreness may persist from few more days to a few months after one of the most acute pain has subsided. Emergencies in the future are more likely to persist lengthier and involve more joints. As the damage resolves, the discomfort will typically lessen. Chronic pain, on the other hand, is not the same as ordinary pain. Even after an effective show in pain reduction, your body will continue to communicate electrical impulses to your consciousness if you have chronic pain. This could also last anywhere from a few weeks to several seasons. Clinical depression can diminish your suppleness, stamina, and fitness, as well as restrict your motion. It may be difficult to do everyday chores as a result of this.
Compounds from your body's immune cells penetrate the blood or tissues during inflammation to defend your system from intruders. This improves blood circulation to the injured or infected region. It might make you feel hot and flushed. Fluid leaks into your cells as a consequence of several of the toxins, causing swelling. This defensive mechanism may produce pain by triggering neurons. This defensive mechanism sometimes produces pain by triggering neurons. Increased leukocyte counts and the substances they produce within your bones cause inflammation, thickening of the joint lining, and articular degradation throughout the years.
Inflammatory response of the synovial membrane is the most common cause of pain, stiffness, and edema in inflammatory arthritis as well as gout type of arthritis. This is referred to as "synovitis." It is indeed important to realize that not every joint is created equal. They come in a variety of shapes and sizes, as well as the types of movement they allow.
A bone is said to have a restricted physical function if it cannot rotate completely and freely in its usual position. A structural defect inside the joint, inflammation of material around the joint, muscular stiffness, discomfort, or illness can all limit mobility. The external rotation of a component relates to both the range and the angle at which it may extend. For many joints and muscles, there have been defined ranges that physicians regard adequate.
A typical knee, for example, ought to be able to flex (bend) within 133 and 153 degrees. In addition, a typical knee must be able to extend absolutely straight.
Limited range of motion results in a decrease in the usual range of motion from any of the joints. The joint range of movement diminishes with aging, but it can also be caused by a variety of diseases, and gout is one of them.
Some of the other causes behind the restricted range of motion include ankylosing spondylitis, cerebral palsy, sepsis, syphilis, Leg-Calve-Perthes disease, juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, etc.
Just like any other disease, if left untreated for quite some time as well with no proper medical assistance and attention, gout can develop into a severe complication over time. Some of those complications are listed below:
Several individuals may not have to deal with gout discomfort again. Others will have gout on many occasions during the year. In patients with recurrent hyperuricemia, medications may help avoid episodes. Gout, if left untreated, can induce severe erosion and damage. Gout might return over the next few months or even years. When it's not treated, it may return increasingly frequently. You may also have to take uric formaldehyde medication if you have repeated attacks or increased concentrations of uric acid in the body. Recurrent gout episodes, if left unchecked, can permanently alter your joints and limit your flexibility.
Persistent gout can lead to the formation of immune complex formations under the epidermis, which are known as tophi (TOE-fie). Tophi can appear anywhere on your body, including your fingertips, wrists, toes, shoulders, and the Rotator cuffs at the backs of your heels. Tophi are typically painless, although they can swell and become sensitive following gout episodes.
Urine is produced when your kidneys eliminate waste and fluid from your blood. When you have more than enough of particular wastes within your bloodstream and not enough hydration, these toxins might pile up in your kidneys and clump collectively. Kidney stones are aggregates of waste that form in the kidneys. When gout progresses, our kidneys are in charge of excreting metabolic acidosis from your body. However, too much and might harm the kidneys. Gouty kidney, gallstones, and kidney failure are all symptoms of gout, as well as indicators that gout is growing worse.
Kidney stones vary in size from a little less than a drop of water to as big as a gemstone. They can either linger in your renal or travel via your urinary bladder ureter (tubes that connect your kidneys and bladder) and very out of your body along with your pee. It's termed releasing a kidney stone whenever a stone travels down your ureters and out your urethral way along with your pee. A kidney pebble can also become lodged in your urinary system, preventing fluid from passing. It can be excruciatingly painful to release a kidney stone or a big kidney stone that prevents the release of your urine.
A mixture of one or more of these techniques can help avoid the build-up of uric acid that causes gout attacks. Medical practitioners are urged to discuss the most effective and attainable preventive methods. Some of the major prevention methods that you can use to avoid gout attacks are mentioned below:
Alcohol significantly reduces the body's natural capacity to eliminate uric acid, putting you at risk for hyperuricemia and a gout attack. A gout attack can be triggered just by one or two cans of beer, champagne, or liquor, and the risk multiplicity of beverages taken. For males and females over the age of 65, excessive or elevated consumption is described as even more than two drinks on every given day or even more than 7 drinks each week, and for males 65 and under, it is described as more than 4 drinks on any given days and perhaps more than 14 beverages per week.
Here are 5 easy ways to help you overcome alcoholism:
Raising your water consumption can assist your kidneys to remain fit and drain uric acid out of your system. The number of fluids that should be consumed each day changes depending on an independent test, weight, ethnicity, and other variables. It is fundamental for overall well-being to drink adequate water to stay hydrated. Dehydration, which may induce sluggish reasoning, mood swings, overheating, dysentery, and gallstones, can all be avoided by drinking enough water.
Although additional study is needed, there is some indication that treating sleep disorders can decrease the prevalence of gout attacks. A continuous positive airway pressure machine or another therapy device that increases oxygen flow during slumber is usually used as part of the treatment. Increased oxygen consumption may reduce the uric acid synthesis and the likelihood of gout attacks.
Gout can be reduced by sustaining weight by diet and exercise. According to studies, rapid, significant weight reduction, including that seen following surgical treatment, may raise the risk of a gout attack in the near term. Excess weight reduction, whether rapid or slow, is an efficient method to lower risk throughout the long run.
Proper nutrition was determined and assessed based on an estimated consumption of nutrients foods such as vegetables, fruits, hazelnuts, whole grains, lean meats, and omega-3 fats, as well as harmful items such as animal-based foods, sugar-sweetened drinks, saturated fat, and salt. To gain proper nutrition, it is important to add healthy food items to your meals and avoid unhealthy food consumption as much as possible.
In this guide, we covered arthritis and its types, gout being the main focus. We included all the possible aspects of indicating as well as preventing gout. If you found this guide helpful, don't forget to share it with your friends and family!
Thank you! Happy prevention!
 |
 |
 |
 |